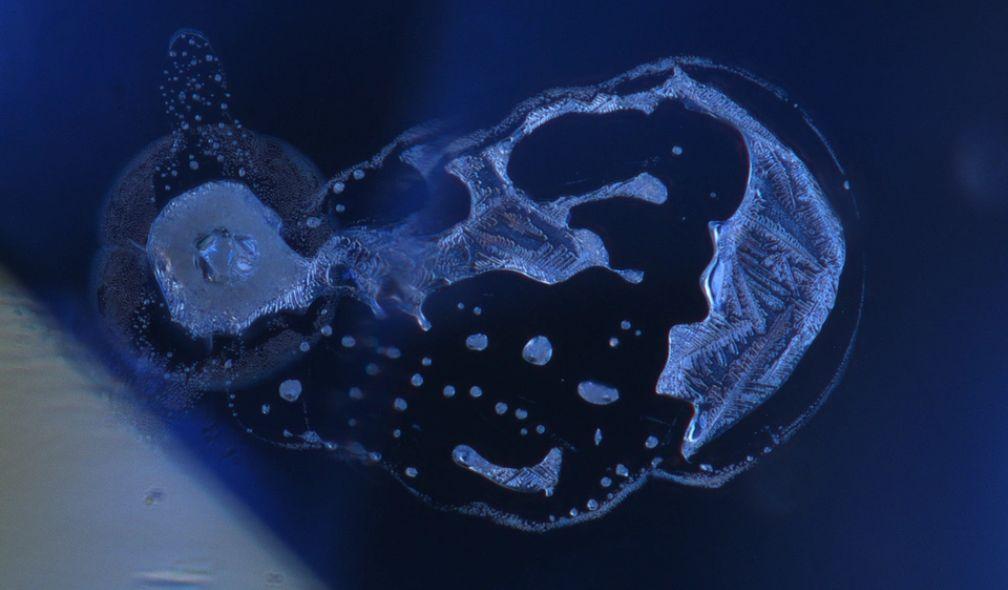
Zircon dramatically altered by high-temperature treatment
Zircon dramatically altered by high-temperature treatment (> 1500 °C). Under the effect of temperature, the zircon (ZrSiO4) dissociated into ZrO2 and SiO2, which are zirconium oxide and silica glass. The glass is amorphous, while the zirconium oxide crystallises. In this micrograph, the zircon crystal was on the left. When the temperature increased, a disc-shaped fracture formed under the combined effect of thermal expansion and metamictisation, which is characteristic of most zircons. Then, during cooling, the molten glass promoted partial healing of the fracture, leaving a few small drops of glass trapped and crystallised zirconium oxide.
- Micrograph : Franck Notari
Do you need this micrograph in full resolution for an article, a DUG dissertation, etc.? Do not hesitate to contact us.
